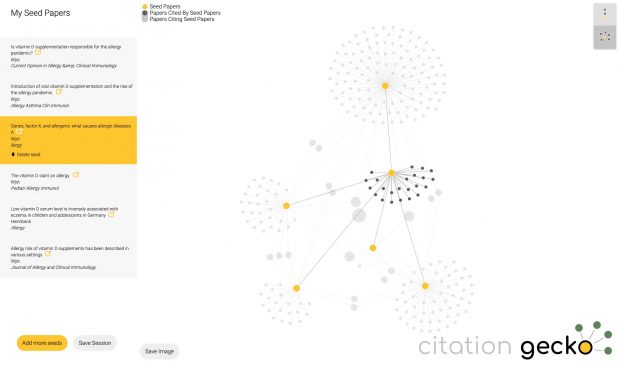
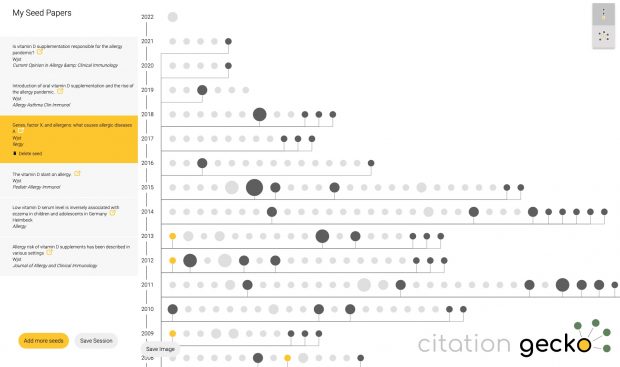
Ich hatte direkt nach der Wende in Halle und Leipzig die erste Ost-West Allergiestudie* durchgeführt und dabei die verblüffende Entdeckung gemacht, dass es im Osten nicht mal halb so häufig Allergien gab.

Der Grund dafür war uns zunächst nicht klar, aber dann stelle sich doch bald heraus, daß es wohl die unterschiedliche Vitamin D Prophylaxe war – im Westen gab es tägliche niedrige Dosen ab der ersten Lebenswoche, im Osten wurde ab dem 2. Monat wenig hohe hohe Einzeldosen verabreicht. Wenn Kinder im Osten krank waren, dann fiel auch immer wieder die eine oder andere Dosis aus, auch wurde das Schema nach meiner Recherche nicht immer komplett durchgezogen. Leider haben wir uns damals aber nur die Impfpässe angesehen, nicht aber die im Nachinein wichtigeren Wiegekarten.

Die Befürchtung der Professoren Mai und Beuren in dem alten SPIEGEL Artikel über Vitamin D Nebenwirkungen haben sich zum Glück nicht bewahrheitet. Dafür aber stellte sich dann aber eine unerwünschte immunologische Wirkung heraus die damals noch nicht bekannt war.
Mit dem aus England bzw Amerika importierten Schema zur Supplementierung stiegen die Allergien an. In der BRD war das ab den frühen 60er Jahren , wie überhaupt die englischsprachigen Länder immer die höchsten Allergiehäufigkeiten hatten, da sie wegen der häufigen Rachitis auch viel konsequenter supplementierten (die Rachitis hiess früher einmal auch “englische Krankheit”).
Mit dem Mauerfall 1989 setzte der Anstieg dann auch in der ex DDR ein und erreichte nach 10, 20 Jahre das Westniveau . Leider wurden unsere Warnungen vor einer zu frühen Supplementierung nicht ernst genommen, der Osten Deutschlands hat – wie so vieles andere auch – das Schema aus dem Westen übernommen und den Preis dafür mit ebenfalls hohen Allergieraten bezahlt.
Der Mechanismus der Allergieentstehung ist dabei nur teilweise aufgeklärt: Vitamin D ist jedenfalls immunsuppressiv mit vielfacher Auswirkung auf B und T Zellen was seit dem Nachweis des Vitamin D Rezeptors auf diesen Immunzellen wissen. Die Supplementierung stört offensichtlich die initiale Klassifikation ob ein Protein harmlos oder allergen ist.
Warum es aber auch schon 1989 Allergien im Osten gab? Nun, es war ja keine Vitamin D freie Zone, offensichtlich sensibilisiert man sich auch noch ausserhalb des überkritischen Intervals in den ersten Lebenswochen.